In 1956, at a workshop held at Dartmouth College in Hanover, New Hampshire, the term “artificial intelligence” was officially coined. Since then, AI and data management have developed in tandem. To perform meaningful and reliable analysis, AI requires vast amounts of big data. Conversely, managing large volumes of data digitally is heavily reliant on AI. Thus, as computing power and database technologies have advanced, so too has AI.
Whereas past business systems could handle only a few gigabytes of data, today’s systems can manage terabytes and use AI to process results and insights in real time. Unlike the man-made “monsters” of old, AI technology is flexible, agile, and responsive, designed to assist and enhance human capabilities rather than replace them.
Three Types of Artificial Intelligence
AI is one of the fastest-evolving technological fields. Today, even the most complex AI models employ only the most basic type of AI, known as “narrow AI.” The other two types exist only in science fiction and are not yet achievable with current AI technology. However, given the rapid pace of development in computer science over the past 50 years, it is difficult to predict where AI will lead us in the future.
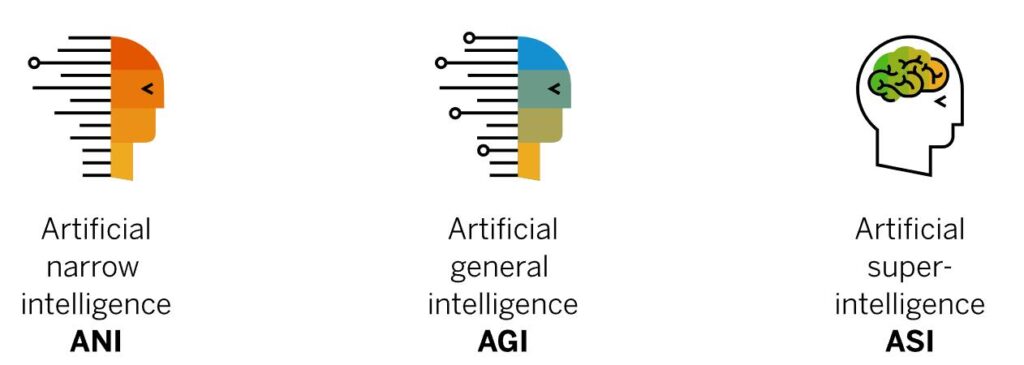
The Three Main Types of AI
Narrow Artificial Intelligence (ANI)
ANI is the form of AI that current technology can achieve, also known as weak AI. Although the tasks performed by narrow AI may be driven by highly complex algorithms and neural networks, they remain single-purpose and goal-oriented. Facial recognition, web searches, and self-driving cars are examples of narrow AI. Narrow AI is classified as weak AI not because of its limited application scope and capability but because it falls far short of the true intelligence characteristic of human traits. Philosopher John Searle posits that narrow AI “can be used to test hypotheses about minds but are not themselves minds.”
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
AGI can successfully perform intellectual tasks that humans can accomplish. Like narrow AI systems, AGI systems can learn from experience, discover patterns, and make predictions. However, AGI’s level of intelligence is superior, capable of extrapolating knowledge from previously acquired data or unsolved tasks and situations.
Summit, one of the world’s few supercomputers that can demonstrate AGI, can perform 200 quadrillion calculations per second—a feat that would take a human a billion years. For practical purposes, an AGI model does not need such immense computational power; it only needs to match the capabilities of current supercomputers.
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI)
Theoretically, ASI systems would possess full self-awareness. Beyond simply mimicking or understanding human behavior, they would fundamentally grasp human actions.
ASI would not only have these human traits but also vastly superior processing and analytical abilities, presenting a dystopian sci-fi future where humans could be rendered obsolete.
While people today may not witness such a world, the rapid advancement of AI suggests that it could eventually surpass human capabilities in nearly all measurable domains. Thus, it is crucial to consider the ethical guidelines and management of AI. As Stephen Hawking warned, “Given the immense potential of AI, it is crucial to research how to reap its benefits while avoiding its potential pitfalls.